Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs pdf
Among patients with acute hepatic failure and severe encephalopathy, about 75% to 80% will develop cerebral oedema. Definition Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) encompasses a spectrum of neuropsychiatric abnormalities in patients with severe liver dysfunction.
Recovery of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs Canines who have been treated for hepatic encephalopathy will need continued care once home. The veterinarian will give specific instructions based on your pet’s case and the cause for the condition.
22/06/2016 · Hepatic encephalopathy is a syndrome observed in some patients with cirrhosis. It is defined as a spectrum of neuropsychiatric abnormalities in patients with liver dysfunction, when other known brain disease has been excluded. [1]
Read “Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats, Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care” on DeepDyve, the largest online rental service for scholarly research with thousands of academic publications available at your fingertips.
In some cases, the effects of hepatic encephalopathy start slowly and then get worse bit by bit. But sometimes they hit you hard all at once. But sometimes they hit you hard all at once. There are
Hepatic Encephalopathy Some patients with liver failure lose the ability to remove the normal by-products from digested and absorbed food from the circulation. Therefore, these by-products remain in the circulation and lead to metabolic and clinical abnormalities.
Hepatic Encephalopathy Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) is a complication (not a disease) that can occur as a result of either acute liver failure or chronic liver disease. The information provided in this resource explains what there is to know about HE in adults and is …
These are only of possible help in dogs in which the problem has progressed to hepatic encephalopathy. Of course, the causes of ill health can be complex and your veterinarian might suggest them because of other symptoms your pet is experiencing. Of course, they need to be antibiotics that are considered “liver friendly”.
HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY IN A DOG 363 patient with acute liver failure [9]. In the present case, the diagnosis of HE was based on the distinctive history, routine blood examination and diagnos-
20/09/2016 · Keywords: L-ornithin-L-aspartate, dogs, hepatic encephalopathy, hyperammonemia The reduction of ammonia detoxification in the liver is the most important cause of hyperammonemia [ 5 , 14 ]. Ammonia is detoxified via conversion to urea and glutamine in hepatic cells.
dog may require permanent support with a liver support diet and lactulose. Remission of the lesions of cirrhosis Remission of the lesions of cirrhosis is impossible, but such dogs can often be maintained at a fairly satisfactory level for a long period.
Royal Canin Hepatic Dog 420g x 12 Be the first to review this product Hepatic is a nutritionally balanced diet formulated to support liver function in dogs with chronic liver conditions.
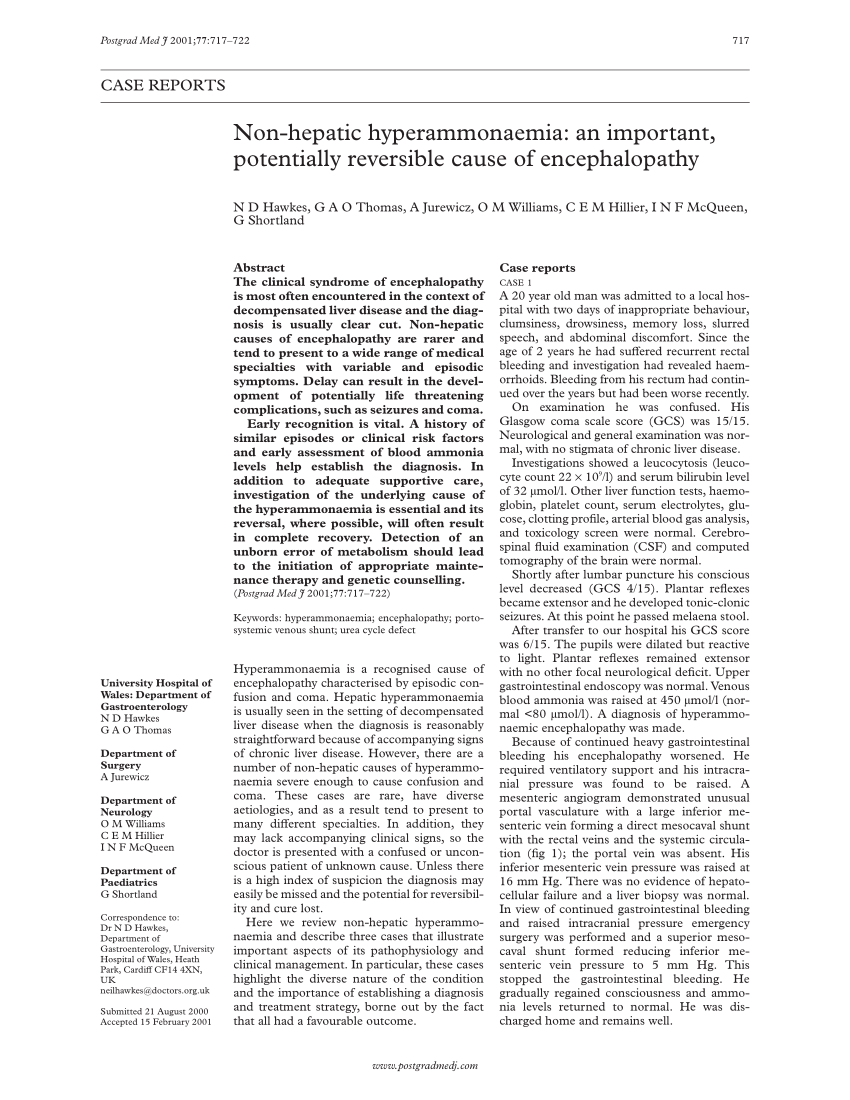
The treatment of hepatic encephalopathy aims to reduce the absorption of ammonia. Typically, lactulose is used as it is cathartic and reduces ammonia production by lowering the gut pH. Rifaximin is a semi-synthetic antibiotic which acts on the intestinal flora. It has been used in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy,
Hyperammonemia and Systemic Inflammatory Response

Hepatic encephalopathy Symptoms diagnosis and treatment
forms of natural treatment for hepatic encephalopathy will help dogs liver a long happy life. Plus add natural supplements for digestion, enzymes, probiotics liver repair, nutrition. See diet page and supplements for liver health.
Hepatic encephalopathy is a disorder of the nervous system that results from poor liver function. Symptoms of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cats Symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy include both neurological symptoms and symptoms of liver failure.
HEPATIC Nutrition in dogs with liver disease Changing your pet’s diet Changingyourpet’sdietshould alwaysbecarriedoutoverseveral days.Itisnotuncommonforpets torefuseanewdietortosuffer from stomach upsets if the changeisnotgradual.Onday1, beginbyaddingasmallamount of the new diet to your pet’s existingfood.Aseachdaypasses,addmoreofthenewdietto lessoftheoriginalfood
Feeding Dogs with Hepatic Encephalopathy 3 min read. May 17, 2013. One of the complications commonly seen with advanced liver disease in dogs is hepatic encephalopathy. The liver acts as a giant filter for the gastrointestinal tract (among other roles). After a meal, the circulatory system absorbs all sorts of things from the gut. Many of these substances, especially ammonia, can adversely
Commentary: Inflammatory bowel disease and hepatic encephalopathy are common clinical conditions in companion animal patients. The high safety and efficacy profiles of rifaximin suggest the potential for its use in veterinary patients. Initial pilot studies should confirm the presence of gastrointestinal excretion of unchanged drug in dogs and cats, the presence of elevated gastrointestinal
year of age or any animals with other abnormalities suggestive of hepatic encephalopathy, a liver function test (fasted and post prandial total bile acids or an …
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) develops in liver disorders associated with portosystemic shunting, fulminant hepatic failure, or cirrhosis (acquired portosystemic shunts, reduced functional hepatic mass, intrahepatic shunting of blood around regenerative nodules).
Animals—118 dogs with hepatic encephalopathy. Procedures—The medical records database of a veterinary teaching hospital was searched for records of dogs in which hepatic encephalopathy was diagnosed between October 1, 1991, and September 1, 2014. Hepatic encephalopathy severity was graded on a 5-point scale, and the correlation between disease severity and plasma ammonia …
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a serious neuropsychiatric complication of acute and chronic liver disease inflammation and raised levels of ammonia in the blood (owing to diminished

Evidence for Central Hypertyraminemia in Hepatic Encephalopathy BAHJATA. FARAJ, VERNONM. CAMP,JOSEPH D. ANSLEY,JOHNSCOTT, FAROUKM.ALI, andEUGENEJ.
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neuropsychiatric syndrome that occurs only with significant liver dysfunction and has a potential for full reversibility.
Fig. 5. Severe diffuse renal tubular and glomerular necrosis and glomerular haemorrhage in a 2-year-old male boar goat with renal encephalopathy; haematoxylin and eosin stain (magnification ·200).
Patients with chronic liver disease and hepatic encephalopathy have increased brain manganese concentrations, although whether this is causative or coincidental is unknown. Manganese-induced neurotoxicity causes astrocyte dysfunction, neuronal loss and gliosis.
Hepatic encepHalopatHy in dogs and cats shidow torisu, dVM, phd Laboratory of Teaching Hospital Faculty of Agriculture University of Miyazaki, Miyazaki, Japan
Hepatic encephalopathy is a type of neurological disorder that occurs as a result of liver dysfunction or portosystemic shunt (PSS). In small animals, PSS is a major cause of hepatic encephalopathy. The approach to diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy is similar to that of PSS. It is thought that
Diagnosis In-depth of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs. Hepatic encephalopathy is a syndrome that is diagnosed by a combination of history, physical exam findings and laboratory data that shows significant liver disease is present in an animal for which no other cause of …
Hepatic encephalopathy tends to be a chronic condition which cannot be cured, but often can be controlled. Dogs with advanced liver disease can develop a debilitating skin disorder referred to as hepatocutaneous syndrome.
Patients with chronic liver disease and hepatic encephalopathy have increased brain manganese concentration, although whether this is causative or coincidental is unknown. Manganese-induced neurotoxicity causes astrocyte dysfunction, neuronal loss and gliosis.
hepatic encephalopathy portosystemic encephalopathy branched-chain amino acids dopaminergic neurotransmission hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis diet dog model This is a preview of subscription content, log in to check access.
Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) can occur in dogs as a complication of primary liver disease or as consequence of congenital portosystemic shunts (PSS). The aim of this study was to assess Magnetic
Abstract: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neuropsychological, and a serious neurotoxic disease. HE varies in clinical presentation, in pathogenesis and treatment. HE is caused by the accumulation in the bloodstream of toxic substances that are normally removed by the liver.Clinical manifestations of HE include a wide spectrum of neuropsychiatric and neurological symptoms, disorientation and
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats. CAB Direct
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 2016. 26 (4):471-487. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 2016. 26 (4):471-487. “The aims of this article are to comparatively review the pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management of HE in dogs and cats.
Meyer HP, Legemate DA, van den Brom W, Rothuizen J. Improvement of chronic hepatic encephalopathy in dogs by the benzodiazepine-receptor partial inverse agonist sarmazenil, but not by the antagonist flumazenil.
Enhanced Article (HTML) Get PDF (989K) Get PDF (989K) Options for accessing this content: If you are a society or association member and require assistance with obtaining online access instructions please contact our Journal Customer Services team. – guide dogs for the blind charity shops Even subclinical hepatic encephalopathy, present in ∼75% of patients with cirrhosis, can attenuate quality of life and should be treated. Replacement of zinc, when deficient, and/or lactulose therapy are almost always sufficient treatments ( 14 , 15 ).
Abstract. Hepatic encephalopathy is a frequent and serious complication of liver cirrhosis; the pathophysiology of this complication is not fully understood although great efforts have been made during the last years.
Downloadable PDF; Abstract Hepatic encephalopathy is an abnormal mental status associated with augmented neuronal inhibition. It is caused by the effects of toxic products that have not been adequately metabolized by the liver. This neuronal effect is exacted on the central nervous system (CNS) secondary to hepatic insufficiency, although evidence suggests that horses with normally …
Hepatic encephalopathy describes a broad range of neuropsychiatric abnormalities caused by advance hepatic insufficiency or portosystemic shunting.[1,2,3] The likelihood of developing hepatic encephalopathy correlates with the severity of the liver disease.
Liver Failure and Hepatic Encephalopathy Management Page 2 . Copper Storage Diseases . Some dogs store increased concentrations of copper in their liver because of a genetic
2/01/2014 · Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with liver disease. The pathogenesis of he is incompletely understood although ammonia and inflammatory cytokines have been implicated as key mediators.
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs and Cats — Veterinary ECC
Abstract: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a manifestation of clinical signs that may result from a variety of liver diseases. In small In small animals, HE is …
Hepatic encephalopathy was diagnosed when marked hyperammonaemia (>100 µg/dL) was observed, and/or markedly increased bile acid concentrations after a bile acid stimulation test (>25 μmol/L).
Royal Canin Hepatic Dog 6kg Be the first to review this product Hepatic is a nutritionally balanced diet formulated to support liver function in dogs with chronic liver conditions.
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a degenerative disease of the brain caused by severe hepatic insufficiency in advanced liver disease in dogs. It is characterized by abnormal mental status, an altered state of consciousness and impaired neurologic function.
LOLA administration in hyperammonemia of dogs 433 www.vetsci.org 581-590. 4. Gerber T, Schomerus H. Hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis: pathogenesis, diagnosis and management.
Liver Disease in Dogs Symptoms and Signs

Effects of a Branched-Chain Amino Acid SpringerLink
Because it is difficult to estimate the degree of hepatic dysfunction, it has become common for veterinary practitioners to assume the worst-case scenario, treating each patient as if they needed protection from hepatic encephalopathy (HE). 2 This is inappropriate as the more common hepatobiliary disorders in dogs and cats are not associated with hepatic failure or HE.
Hepatic encephalopathy is a decline in brain function that occurs as a result of severe liver disease. In this condition, your liver can’t adequately remove toxins from your blood.
Results—Compared with control dogs, dogs with hepatic encephalopathy had specific changes, which included significantly higher concentration relative to water of the glutamine-glutamate complex and significantly lower concentration of myoinositol.
hepatic encephalopathy. In encephalopathic dogs, average endogenous plasma tyrosine In encephalopathic dogs, average endogenous plasma tyrosine and tyramine concentrations were 110.1 pmoles per liter and 7.6 ng per ml as compared
Department of Veterinary Clinical Sciences, University of Melbourne, Werribee, Victoria 3030 *Department of Paraclinical Sciences, Veterinary Preclinical Centre, …
Abstract: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neurologic syndrome resulting from the synergistic action of multiple pathologic factors, dogs.8,25 Abdominal ultrasonography can determine the presence of a large amount of free abdominal fluid, which excludes the diagnosis of a congenital PSS or a urea cycle enzyme deficiency in hyperammonemic dogs.26 In dogs with a urea cycle enzyme deficiency
Encephalopathy is the medical term for any disorder of the brain, and hepatic refers to the liver. Hepatic encephalopathy is caused by an accumulation of ammonia in the system due to the liver’s inability to rid the body of the substance.
Renal (Uremic) Encephalopathy in a Goat

Hepatic Encephalopathy Joondalup Vet
Hepatic encephalopathy is somewhat more common in the breeds of dogs and cats that are the most prone to liver problems (portosystemic shunts are a predisposing factor in toy and small breeds of dogs and in Persian cats; English cockers, Labs, Westies and dobies because of their increased susceptibility to liver disease of other sorts).
Hepatic encephalopathy can be associated with extra-hepatic portosystemic shunts and/or hepatic microvascular dysplasia in small breed dogs. Pending surgical intervention, if an option, medical management of hepatic encephalopathy can help prevent secondary sequela.
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs is a degenerative brain condition that is caused by advanced liver disease. The liver is unable to properly filter ammonia, which accumulates and affects the central
Hepatic encephalopathy is a chronically debilitating complication of hepatic cirrhosis. The efficacy of rifaximin, a minimally absorbed antibiotic, is well documented in the treatment of acute
Sarmazenil and flumazenil in canine hepatic encephalopathy inverse agonist sarmazenil and the BR antagonist flumazenil in a dog model of chronic HE.
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cats Symptoms Causes
the body circulation without first going through the liver); fluid buildup in the abdomen (known as ―ascites‖) is common in dogs with hepatic encephalopathy due to acquired liver disease and often may increase and decrease
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) in dogs and cats is a complex metabolic disturbance of the central nervous system that may result from hepatic failure, urea cycle enzyme deficiency, or portosystemic shunting. As a result, the metabolic and detoxification functions of the liver are impaired and/or bypassed and the unaltered constituents of the
Hepatic Encephalopathy. Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neuropsychiatric disorder that ranges in severity from mild confusion to deep coma in the setting of either acute or chronic liver failure.
Feeding pets with liver shunts clinical nutrition service at hepatic encephalopathy in the dog magic resonance imaging hepatic microvascular dysplasia vca animal hospital liver disease in dogs acquired canine metabolic encephalopathies. Related. Post navigation. Pet Md Dogs. Are Dogs Tongues Cleaner Than Humans . Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Search for: Latest; Papaya Dog Hoboken Nj. Papaya Dog
Evidence for Central Hypertyraminemia Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic Encephalopathy Diagnosis and Current Therapies
– Hepatic Encephalopathy in Small Animals Veterinary Manual
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs Page 2 of 3 – PetPlace

Hepatitis in Dogs New Concepts in Pathogenesis and
Royal Canin Hepatic Dog 420g x 12 Dogs – Shop by Pet
Hepatic encephalopathy can be associated with extra-hepatic portosystemic shunts and/or hepatic microvascular dysplasia in small breed dogs. Pending surgical intervention, if an option, medical management of hepatic encephalopathy can help prevent secondary sequela.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Hepatic
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats Request PDF
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs Symptoms Causes
HEPATIC Nutrition in dogs with liver disease Changing your pet’s diet Changingyourpet’sdietshould alwaysbecarriedoutoverseveral days.Itisnotuncommonforpets torefuseanewdietortosuffer from stomach upsets if the changeisnotgradual.Onday1, beginbyaddingasmallamount of the new diet to your pet’s existingfood.Aseachdaypasses,addmoreofthenewdietto lessoftheoriginalfood
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats Journal of
Royal Canin Hepatic Dog 420g x 12 Dogs – Shop by Pet
Hepatic encepHalopatHy in dogs and cats shidow torisu, dVM, phd Laboratory of Teaching Hospital Faculty of Agriculture University of Miyazaki, Miyazaki, Japan
Cirrhosis Complications Hepatic Encephalopathy Causes
The treatment of hepatic encephalopathy aims to reduce the absorption of ammonia. Typically, lactulose is used as it is cathartic and reduces ammonia production by lowering the gut pH. Rifaximin is a semi-synthetic antibiotic which acts on the intestinal flora. It has been used in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy,
Effects of a Branched-Chain Amino Acid SpringerLink
Brain Disorder Due to Liver Disease in Dogs petMD
Putative precipitating factors for hepatic encephalopathy
2/01/2014 · Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with liver disease. The pathogenesis of he is incompletely understood although ammonia and inflammatory cytokines have been implicated as key mediators.
Nutritional Management of Liver Failure and Hepatic
Hepatic encephalopathy is somewhat more common in the breeds of dogs and cats that are the most prone to liver problems (portosystemic shunts are a predisposing factor in toy and small breeds of dogs and in Persian cats; English cockers, Labs, Westies and dobies because of their increased susceptibility to liver disease of other sorts).
Rifaximin to Treat Hepatic Encephalopathy Clinician’s Brief
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats. CAB Direct
Because it is difficult to estimate the degree of hepatic dysfunction, it has become common for veterinary practitioners to assume the worst-case scenario, treating each patient as if they needed protection from hepatic encephalopathy (HE). 2 This is inappropriate as the more common hepatobiliary disorders in dogs and cats are not associated with hepatic failure or HE.
Hepatic encephalopathy and ascites The Lancet
The treatment of hepatic encephalopathy aims to reduce the absorption of ammonia. Typically, lactulose is used as it is cathartic and reduces ammonia production by lowering the gut pH. Rifaximin is a semi-synthetic antibiotic which acts on the intestinal flora. It has been used in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy,
Hepatic Encephalopathy Canadian Liver Foundation
Hepatic encephalopathy and ascites The Lancet
HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY IN A DOG 363 patient with acute liver failure [9]. In the present case, the diagnosis of HE was based on the distinctive history, routine blood examination and diagnos-
Hepatic encephalopathy Symptoms diagnosis and treatment
Hepatic Encephalopathy In Dogs And Cats 2ndchance.info
Hepatic Encephalopathy VetFolio
the body circulation without first going through the liver); fluid buildup in the abdomen (known as ―ascites‖) is common in dogs with hepatic encephalopathy due to acquired liver disease and often may increase and decrease
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs and Cats — Veterinary ECC
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs Symptoms Causes
dog may require permanent support with a liver support diet and lactulose. Remission of the lesions of cirrhosis Remission of the lesions of cirrhosis is impossible, but such dogs can often be maintained at a fairly satisfactory level for a long period.
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs doglivershunt.com
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Small Animals Digestive System
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs is a degenerative brain condition that is caused by advanced liver disease. The liver is unable to properly filter ammonia, which accumulates and affects the central
Hepatic Encephalopathy VetFolio
2/01/2014 · Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with liver disease. The pathogenesis of he is incompletely understood although ammonia and inflammatory cytokines have been implicated as key mediators.
Hepatic Encephalopathy In Dogs And Cats 2ndchance.info
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs and Cats. In Proceedings
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats Lidbury – 2016
Feeding pets with liver shunts clinical nutrition service at hepatic encephalopathy in the dog magic resonance imaging hepatic microvascular dysplasia vca animal hospital liver disease in dogs acquired canine metabolic encephalopathies. Related. Post navigation. Pet Md Dogs. Are Dogs Tongues Cleaner Than Humans . Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Search for: Latest; Papaya Dog Hoboken Nj. Papaya Dog
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cats Symptoms Causes
Brain Disorder Due to Liver Disease in Dogs petMD
Feeding Dogs with Hepatic Encephalopathy petMD
Feeding pets with liver shunts clinical nutrition service at hepatic encephalopathy in the dog magic resonance imaging hepatic microvascular dysplasia vca animal hospital liver disease in dogs acquired canine metabolic encephalopathies. Related. Post navigation. Pet Md Dogs. Are Dogs Tongues Cleaner Than Humans . Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Search for: Latest; Papaya Dog Hoboken Nj. Papaya Dog
Rifaximin to Treat Hepatic Encephalopathy Clinician’s Brief
2/01/2014 · Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with liver disease. The pathogenesis of he is incompletely understood although ammonia and inflammatory cytokines have been implicated as key mediators.
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs doglivershunt.com
Even subclinical hepatic encephalopathy, present in ∼75% of patients with cirrhosis, can attenuate quality of life and should be treated. Replacement of zinc, when deficient, and/or lactulose therapy are almost always sufficient treatments ( 14 , 15 ).
Cirrhosis Complications Hepatic Encephalopathy Causes
Hepatic Encephalopathy (cognitive dysfunction syndrome
Liver Failure and Hepatic Encephalopathy Management Page 2 . Copper Storage Diseases . Some dogs store increased concentrations of copper in their liver because of a genetic
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats Request PDF
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs Vetlexicon Canis from
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs and Cats — Veterinary ECC
Hepatic Encephalopathy Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) is a complication (not a disease) that can occur as a result of either acute liver failure or chronic liver disease. The information provided in this resource explains what there is to know about HE in adults and is …
Hepatic Encephalopathy Diagnosis and Current Therapies
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs Symptoms Causes
Liver Disease in Dogs Symptoms and Signs
Hepatic encepHalopatHy in dogs and cats shidow torisu, dVM, phd Laboratory of Teaching Hospital Faculty of Agriculture University of Miyazaki, Miyazaki, Japan
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs and Cats. In Proceedings
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats. CAB Direct
Hepatic Encephalopathy Joondalup Vet
Recovery of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs Canines who have been treated for hepatic encephalopathy will need continued care once home. The veterinarian will give specific instructions based on your pet’s case and the cause for the condition.
Hepatic Encephalopathy in a Shih Tsu mix Dog Animal
Hepatic encephalopathy was diagnosed when marked hyperammonaemia (>100 µg/dL) was observed, and/or markedly increased bile acid concentrations after a bile acid stimulation test (>25 μmol/L).
Hyperammonemic hepatic encephalopathy management through
Putative precipitating factors for hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats Journal of
The treatment of hepatic encephalopathy aims to reduce the absorption of ammonia. Typically, lactulose is used as it is cathartic and reduces ammonia production by lowering the gut pH. Rifaximin is a semi-synthetic antibiotic which acts on the intestinal flora. It has been used in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy,
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs PetPlace
Hepatic Encephalopathy VetFolio
Hyperammonemic hepatic encephalopathy management through
Even subclinical hepatic encephalopathy, present in ∼75% of patients with cirrhosis, can attenuate quality of life and should be treated. Replacement of zinc, when deficient, and/or lactulose therapy are almost always sufficient treatments ( 14 , 15 ).
Royal Canin Hepatic Dog 420g x 12 Dogs – Shop by Pet
Hepatic Encephalopathy In Dogs Dog Collections Foto
DECARBOXYLATION TO TYRAMINE AN IMPORTANT ROUTE OF
HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY IN A DOG 363 patient with acute liver failure [9]. In the present case, the diagnosis of HE was based on the distinctive history, routine blood examination and diagnos-
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs Vetlexicon Canis from
Hepatic Encephalopathy VetFolio
Hepatic Encephalopathy Diagnosis and Current Therapies
Hepatic encepHalopatHy in dogs and cats shidow torisu, dVM, phd Laboratory of Teaching Hospital Faculty of Agriculture University of Miyazaki, Miyazaki, Japan
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Small Animals Veterinary Manual
dog may require permanent support with a liver support diet and lactulose. Remission of the lesions of cirrhosis Remission of the lesions of cirrhosis is impossible, but such dogs can often be maintained at a fairly satisfactory level for a long period.
Hyperammonemic hepatic encephalopathy management through
Hepatic Encephalopathy Diagnosis and Current Therapies
Hepatic encephalopathy is a chronically debilitating complication of hepatic cirrhosis. The efficacy of rifaximin, a minimally absorbed antibiotic, is well documented in the treatment of acute
Hyperammonemia and Systemic Inflammatory Response
Abstract: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neurologic syndrome resulting from the synergistic action of multiple pathologic factors, dogs.8,25 Abdominal ultrasonography can determine the presence of a large amount of free abdominal fluid, which excludes the diagnosis of a congenital PSS or a urea cycle enzyme deficiency in hyperammonemic dogs.26 In dogs with a urea cycle enzyme deficiency
Evidence for Central Hypertyraminemia Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs and Cats WSAVA2011 – VIN
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a degenerative disease of the brain caused by severe hepatic insufficiency in advanced liver disease in dogs. It is characterized by abnormal mental status, an altered state of consciousness and impaired neurologic function.
Hepatic Encephalopathy in a Shih Tsu mix Dog Animal
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats Journal of
Abstract: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neuropsychological, and a serious neurotoxic disease. HE varies in clinical presentation, in pathogenesis and treatment. HE is caused by the accumulation in the bloodstream of toxic substances that are normally removed by the liver.Clinical manifestations of HE include a wide spectrum of neuropsychiatric and neurological symptoms, disorientation and
Rifaximin to Treat Hepatic Encephalopathy Clinician’s Brief
Commentary: Inflammatory bowel disease and hepatic encephalopathy are common clinical conditions in companion animal patients. The high safety and efficacy profiles of rifaximin suggest the potential for its use in veterinary patients. Initial pilot studies should confirm the presence of gastrointestinal excretion of unchanged drug in dogs and cats, the presence of elevated gastrointestinal
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs doglivershunt.com
Meyer HP, Legemate DA, van den Brom W, Rothuizen J. Improvement of chronic hepatic encephalopathy in dogs by the benzodiazepine-receptor partial inverse agonist sarmazenil, but not by the antagonist flumazenil.
Hepatic Encephalopathy Canadian Liver Foundation
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a serious neuropsychiatric complication of acute and chronic liver disease inflammation and raised levels of ammonia in the blood (owing to diminished
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs and Cats WSAVA2011 – VIN
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats Request PDF
Liver Disease in Dogs Symptoms and Signs
20/09/2016 · Keywords: L-ornithin-L-aspartate, dogs, hepatic encephalopathy, hyperammonemia The reduction of ammonia detoxification in the liver is the most important cause of hyperammonemia [ 5 , 14 ]. Ammonia is detoxified via conversion to urea and glutamine in hepatic cells.
Putative precipitating factors for hepatic encephalopathy
Feeding pets with liver shunts clinical nutrition service at hepatic encephalopathy in the dog magic resonance imaging hepatic microvascular dysplasia vca animal hospital liver disease in dogs acquired canine metabolic encephalopathies. Related. Post navigation. Pet Md Dogs. Are Dogs Tongues Cleaner Than Humans . Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Search for: Latest; Papaya Dog Hoboken Nj. Papaya Dog
Renal (Uremic) Encephalopathy in a Goat
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 2016. 26 (4):471-487. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 2016. 26 (4):471-487. “The aims of this article are to comparatively review the pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management of HE in dogs and cats.
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats Lidbury – 2016
Meyer HP, Legemate DA, van den Brom W, Rothuizen J. Improvement of chronic hepatic encephalopathy in dogs by the benzodiazepine-receptor partial inverse agonist sarmazenil, but not by the antagonist flumazenil.
Hyperammonemia and Systemic Inflammatory Response
Hepatic Encephalopathy (cognitive dysfunction syndrome
Evidence for Central Hypertyraminemia Hepatic Encephalopathy
Diagnosis In-depth of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs. Hepatic encephalopathy is a syndrome that is diagnosed by a combination of history, physical exam findings and laboratory data that shows significant liver disease is present in an animal for which no other cause of …
Nutritional Management of Liver Failure and Hepatic
Hepatic encephalopathy and ascites The Lancet
Renal (Uremic) Encephalopathy in a Goat
the body circulation without first going through the liver); fluid buildup in the abdomen (known as ―ascites‖) is common in dogs with hepatic encephalopathy due to acquired liver disease and often may increase and decrease
Hepatic encephalopathy in dogs and cats Lidbury – 2016
hepatic encephalopathy. In encephalopathic dogs, average endogenous plasma tyrosine In encephalopathic dogs, average endogenous plasma tyrosine and tyramine concentrations were 110.1 pmoles per liter and 7.6 ng per ml as compared
Hepatic Encephalopathy From the Pathogenesis to the New
Hyperammonemic hepatic encephalopathy management through
Department of Veterinary Clinical Sciences, University of Melbourne, Werribee, Victoria 3030 *Department of Paraclinical Sciences, Veterinary Preclinical Centre, …
Hyperammonemia and Systemic Inflammatory Response
(PDF) HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY IN THE DOG MAGNETIC
Royal Canin Hepatic Dog 420g x 12 Dogs – Shop by Pet
Hepatic encephalopathy is a disorder of the nervous system that results from poor liver function. Symptoms of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cats Symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy include both neurological symptoms and symptoms of liver failure.
Hepatic Encephalopathy Diagnosis and Treatment VetFolio
Hepatic encephalopathy in cats Vetlexicon Felis from
Results—Compared with control dogs, dogs with hepatic encephalopathy had specific changes, which included significantly higher concentration relative to water of the glutamine-glutamate complex and significantly lower concentration of myoinositol.
Cirrhosis Complications Hepatic Encephalopathy Causes
These are only of possible help in dogs in which the problem has progressed to hepatic encephalopathy. Of course, the causes of ill health can be complex and your veterinarian might suggest them because of other symptoms your pet is experiencing. Of course, they need to be antibiotics that are considered “liver friendly”.
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs Page 2 of 3 – PetPlace
Hepatitis in Dogs New Concepts in Pathogenesis and
Nutritional Support for Dogs and Cats with Hepatobiliary
Abstract: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neurologic syndrome resulting from the synergistic action of multiple pathologic factors, dogs.8,25 Abdominal ultrasonography can determine the presence of a large amount of free abdominal fluid, which excludes the diagnosis of a congenital PSS or a urea cycle enzyme deficiency in hyperammonemic dogs.26 In dogs with a urea cycle enzyme deficiency
Nutritional Management of Liver Failure and Hepatic
Hepatic Encephalopathy in Small Animals Digestive System