Gas exchange in animals pdf
Lungs and gills are the organs specialized for O2 and CO2 exchange between air or water and blood;in some animals, the skin serves this task, partly or exclusively. Functional characteristics of gas-exchange systems in different vertebrate groups are discussed.
BIOLOGY 90462 Describe diversity in the structure and function of animals GAS EXCHANGE Note: Students are expected to demonstrate understanding of diversity in …
the connection between weight change and gas exchange: Plants gain weight because they are absorbing carbon from the air, and when plants (or animals or decomposers) lose weight, it is primarily because they are losing carbon to the atmosphere.
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS We will be studying the diversity of adaptations for this process in two animal groups: Fish Mammals
1 Animal Diversity Part I Introduction One of the primary goals of the second half of Biol 106 is to understand evolutionary relationships among animals and to gain
How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion • Gas is exchanged between respiratory medium and body fluids through diffusion across a respiratory surface • To effectively exchange gases, the surface must be 1. thin 2. wet How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion • Some animals have no specialized respiratory organs or circulatory systems –O2 obtained through simple diffusion
Gaseous Exchange In Animals. Breathing mechanisms Many animals possess special breathing mechanisms that increase the rate if gaseous exchange between the animals …
B io Factsheet. September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals All living organisms respire. They need to do this so that energy can be transformed into a form that cells can use.
Question Bank Respiratory System 1. Name the following : (i) The condition in which the oxygen supply to the respiratory system is cut off. (ii) The membrane enveloping the lungs. (iii) The part of the tidal air that effectively takes part in the gaseous exchange in the lungs. (iv) Sum total of tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume and expiratory reserve volume. (v) A muscular sheet of
Respiratory System – All About Breathing Your respiratory system is all about exchanging gases with the environment. Some animals such as amphibians are able to exchange …
The gas exchange of water-breathing animals is described in terms of the O 2 and CO 2 tensions. Equations are developed which describe the gill ventilation requirements in terms of gill O 2 and CO 2 tensions, exchange ratio, metabolic rate, and inspired gas tensions.
Chapter 49 Gas Exchange in Animals

GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS Sciencepoint Cafe
active tissues of the animals. 12 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS. Respiration in Plants BIOLOGY 263 Notes MODULE – 2 Forms and Functions of 12.1 RESPIRATION Plants and animals Respiration is the stepwise oxidation of complex organic molecules and release of energy as ATP for various cellular metabolic activities. It involves exchange of gases between the organism and the external …
Fick’s Law of Diffusion • Gas exchange involves the diffusion of gases across a membrane • Rate of diffusion (R) is governed by Fick’s Law:
(b) Table 4.1 describes some of the features of the mammalian gas exchange system. Complete the table by explaining how each feature improves the efficiency of gaseous exchange.
For terrestrial animals and plants, a fundamental cost of living is water vapor lost to the atmosphere during exchange of metabolic gases. Here, by bringing together previously developed models for specific taxa, we integrate properties common to all terrestrial gas exchangers into a universal model
Many frogs use lungs to respire, bringing in air through their nares and mouth, into the trachea and then to the lungs for gas exchange and uptake of oxygen. However, frogs lack the diaphragm that is an anatomical structure present in many other species. The diaphragm is a muscle used to create a pressure gradient to draw air into the lungs. This is
RESPIRATION AND GAS EXCHANGE. Key concepts Types of respiration Cellular Respiration is the chemical breakdown of food substances to yield ATP. Different organisms use different kinds of breathing mechanisms in order to transport oxygen throughout their bodies. Evolutionary adaptations of gas exchange systems and respiration Different plant adaptations in acquiring CO 2 from the …
ADAPTATION I. RESPIRATION: GAS EXCHANGE A. Lungs – An Overview – evolved from swim bladders – ventilation through breathing – passive diffusion of oxygen and CO2
The cutaneous contribution to overall gas exchange is often most important in small animals, at cool temperatures, at low levels of activity and in normoxic and normocapnic conditions. Branchial and pulmonary respiration increasingly predominate in other circumstances.
1 Chapter 49: Gas Exchange in Animals What Physical Factors Govern Respiratory Gas Exchange? What Adaptations Maximize Respiratory Gas Exchange? How does the …
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS 923 species, including some highly efficient ones, such as fish gills and bird lungs, and less efficient ones, such as our own.
23/04/2018 · Gaseous exchange in animals The majority of animals need oxygen in order to oxidize the organic materials and produce energy for cellular activities. The oxidation of the food not only yields energy but also carbon dioxide which must be constantly removed from the body. The process of moving oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide…
Medium flows past gas exchange surface in an unpredictable pattern. In animals that tidally ventilate, PO 2 in the respiratory cavity is lower than the outside medium. Respiratory cavities do not fully empty. Fresh air mixes with oxygen-depleted residual air P O2 of blood equilibrates with the P O2 of the respiratory cavity. Tidal Ventilation . Tidal Ventilation . Unidirectional
The gas exchange surface of a mammal is the alveolus. There are numerous alveoli – air sacs, supplied with gases via a system of tubes (trachea, splitting into two bronchi – one for each lung – and numerous bronchioles) connected to the outside by the mouth and nose.
10 ANIMALS Respiratory System .notebook 2 January 18, 2016 Gas Exchange Respiratory surface = the portion of the animal surface where gas
Exchange of Gases by Animal Respiratory Organs! In small organisms (e.g.. Amoeba, Paramecium) the exchange of gases occurs through the general surface of the body or the cell membrane.
Small animals, such as the mouse, rat, and hamster, have been successfully cooled to complete cardiac arrest and then revived by the use of a closed-chamber technique, whereby gradually increasing environmental levels of carbon dioxide and diminishing levels of oxygen occur concomitantly with cold exposure. 1-5 Similar results have been attained with dog and man inhaling gas mixtures

26/12/2017 · Gas Exchange in Animals Bio Factsheet 2 Fig 2. The alveoli The concentration gradients of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the alveoli are maintained by the highly efficient blood transport of …
Respiration and Gaseous Exchange. A respiratory organ consists of a surface across which gas exchange by diffusion can occur between blood and either water or air The surface must be • moist enough to allow the cells to live • large enough to permit sufficient gas exchange • thin enough to permit rapid diffusion In respiration • blood entering the respiratory organ must be high in CO 2
Gas exchange is the diffusion of these gases into and out of cells, and this is essential for respiration to occur. For diffusion and therefore gas exchange to occur quickly there must be a large surface area
6/12/2013 · Category Education; Song (What A) Wonderful World; Artist Sam Cooke; Album Portrait of a Legend; Writers Herb Alpert, Sam Cooke, Lou Adler
The structural and chemical limitations to respiratory gas exchange existing between the ambient medium and the cell are comprehensively treated. Beginning with an examination of the natural oscillati
plants and animals; irrespective of the location of such cells in the organism. Respiration is an enzyme-controlled process involving the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats and oils and in certain
Vertebrate Gas Exchange SpringerLink
Seagrass-Watch www.seagrasswatch.org Seagrass Educators Handbook By Len McKenzie (Seagrass-Watch HQ/DPI&F), Feb 2008 This handbook provides educators with information on what seagrasses are, their plant morphology and
Gas Exchange/Transpiration . I. Definitions. Transpiration – evaporation of water from a plant surface; Evapotranspiration – evaporation of water from a plant surface and soil (including abiotic surroundings).
21/11/2016 · Biology_b-gas-exch-75.mp4 Class 11-Zoology-Breathing and Exchange of Gases-Online NEET Videos – Duration: 3:40.
Avian Respiration. This page has been so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are shared by alveoli and much of the lung volume. The avian respiratory system is partitioned heterogeneously, so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are separate in the air sacs (shaded in gray) and the parabronchial lung, respectively. Air sacs act as bellows to ventilate the tube-like – animals in the park an abc book pdf Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) and wastes.
A paradox in order to exchange gases for metabolism, animals (and plants) need to have a large surface area means that the areas through which water is lost is also increased. Solutions : put gas absorbing surface in side a humid chamber (i.e., humans lungs)
external gas exchange system would not be suitable for land animals as the moisture would not be able to be maintained due to evaporation and the gill filaments would collapse without the support of water.
B5 Gaseous Exchange in Animals. Larynx – The voice box which makes sound used in speaking. Trachea – The windpipe, it’s held open by rings of cartilage.
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O 2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and wastes.
A respiratory gas exchange catheter: In vitro and in vivo tests in large animals Brack G. Hattler, MD, PhD Laura W. Lund, PhD Joseph Golob, BS Heide Russian, BS
Tissue respiration, gas exchange and breathing MCQs, tissue respiration, gas exchange and breathing quiz answers, learn IGCSE O level biology online courses. Tissue respiration, gas exchange and breathing multiple choice questions and answers pdf on school level biology, human respiration, what is respiration, aerobic respiration and its waste
Frog Animal Respiration
PLANT GROWTH AND GAS EXCHANGE

Biology4Kids.com Animal Systems Respiratory System
A respiratory gas exchange catheter In vitro and in vivo
September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals
Avian Respiration Eastern Kentucky University

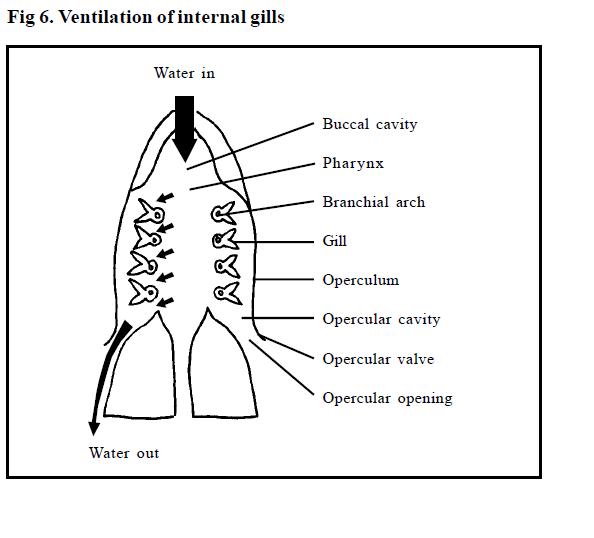
Unit 2 The Variety of Living Organisms Gas Exchange
BIOLOGY 90462 No Brain Too Small
– Please note These are extracts from one student’s response
Animal Diversity Part I Washington State University


GAS EXCHANGE in “Animals”
Tissue Respiration Gas Exchange and Breathing MCQs Quiz
Gas Exchange in Animals marabytanguay.files.wordpress.com
BIOLOGY 90462 No Brain Too Small
How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion • Gas is exchanged between respiratory medium and body fluids through diffusion across a respiratory surface • To effectively exchange gases, the surface must be 1. thin 2. wet How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion • Some animals have no specialized respiratory organs or circulatory systems –O2 obtained through simple diffusion
Seagrass-Watch www.seagrasswatch.org Seagrass Educators Handbook By Len McKenzie (Seagrass-Watch HQ/DPI&F), Feb 2008 This handbook provides educators with information on what seagrasses are, their plant morphology and
Gas Exchange/Transpiration . I. Definitions. Transpiration – evaporation of water from a plant surface; Evapotranspiration – evaporation of water from a plant surface and soil (including abiotic surroundings).
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS We will be studying the diversity of adaptations for this process in two animal groups: Fish Mammals
23/04/2018 · Gaseous exchange in animals The majority of animals need oxygen in order to oxidize the organic materials and produce energy for cellular activities. The oxidation of the food not only yields energy but also carbon dioxide which must be constantly removed from the body. The process of moving oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide…
Avian Respiration. This page has been so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are shared by alveoli and much of the lung volume. The avian respiratory system is partitioned heterogeneously, so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are separate in the air sacs (shaded in gray) and the parabronchial lung, respectively. Air sacs act as bellows to ventilate the tube-like
21/11/2016 · Biology_b-gas-exch-75.mp4 Class 11-Zoology-Breathing and Exchange of Gases-Online NEET Videos – Duration: 3:40.
1 Chapter 49: Gas Exchange in Animals What Physical Factors Govern Respiratory Gas Exchange? What Adaptations Maximize Respiratory Gas Exchange? How does the …
B5 Gaseous Exchange in Animals. Larynx – The voice box which makes sound used in speaking. Trachea – The windpipe, it’s held open by rings of cartilage.
Gas Exchange Animals
Vertebrate Gas Exchange SpringerLink
21/11/2016 · Biology_b-gas-exch-75.mp4 Class 11-Zoology-Breathing and Exchange of Gases-Online NEET Videos – Duration: 3:40.
Gas Exchange/Transpiration . I. Definitions. Transpiration – evaporation of water from a plant surface; Evapotranspiration – evaporation of water from a plant surface and soil (including abiotic surroundings).
The gas exchange of water-breathing animals is described in terms of the O 2 and CO 2 tensions. Equations are developed which describe the gill ventilation requirements in terms of gill O 2 and CO 2 tensions, exchange ratio, metabolic rate, and inspired gas tensions.
Avian Respiration. This page has been so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are shared by alveoli and much of the lung volume. The avian respiratory system is partitioned heterogeneously, so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are separate in the air sacs (shaded in gray) and the parabronchial lung, respectively. Air sacs act as bellows to ventilate the tube-like
How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion • Gas is exchanged between respiratory medium and body fluids through diffusion across a respiratory surface • To effectively exchange gases, the surface must be 1. thin 2. wet How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion • Some animals have no specialized respiratory organs or circulatory systems –O2 obtained through simple diffusion
The gas exchange surface of a mammal is the alveolus. There are numerous alveoli – air sacs, supplied with gases via a system of tubes (trachea, splitting into two bronchi – one for each lung – and numerous bronchioles) connected to the outside by the mouth and nose.
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS We will be studying the diversity of adaptations for this process in two animal groups: Fish Mammals
Tissue respiration, gas exchange and breathing MCQs, tissue respiration, gas exchange and breathing quiz answers, learn IGCSE O level biology online courses. Tissue respiration, gas exchange and breathing multiple choice questions and answers pdf on school level biology, human respiration, what is respiration, aerobic respiration and its waste
Gaseous Exchange In Animals. Breathing mechanisms Many animals possess special breathing mechanisms that increase the rate if gaseous exchange between the animals …
Small animals, such as the mouse, rat, and hamster, have been successfully cooled to complete cardiac arrest and then revived by the use of a closed-chamber technique, whereby gradually increasing environmental levels of carbon dioxide and diminishing levels of oxygen occur concomitantly with cold exposure. 1-5 Similar results have been attained with dog and man inhaling gas mixtures
BIOLOGY 90462 No Brain Too Small
Gas Exchange Animals
23/04/2018 · Gaseous exchange in animals The majority of animals need oxygen in order to oxidize the organic materials and produce energy for cellular activities. The oxidation of the food not only yields energy but also carbon dioxide which must be constantly removed from the body. The process of moving oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide…
Small animals, such as the mouse, rat, and hamster, have been successfully cooled to complete cardiac arrest and then revived by the use of a closed-chamber technique, whereby gradually increasing environmental levels of carbon dioxide and diminishing levels of oxygen occur concomitantly with cold exposure. 1-5 Similar results have been attained with dog and man inhaling gas mixtures
B io Factsheet. September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals All living organisms respire. They need to do this so that energy can be transformed into a form that cells can use.
21/11/2016 · Biology_b-gas-exch-75.mp4 Class 11-Zoology-Breathing and Exchange of Gases-Online NEET Videos – Duration: 3:40.
Question Bank Respiratory System 1. Name the following : (i) The condition in which the oxygen supply to the respiratory system is cut off. (ii) The membrane enveloping the lungs. (iii) The part of the tidal air that effectively takes part in the gaseous exchange in the lungs. (iv) Sum total of tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume and expiratory reserve volume. (v) A muscular sheet of
Avian Respiration. This page has been so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are shared by alveoli and much of the lung volume. The avian respiratory system is partitioned heterogeneously, so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are separate in the air sacs (shaded in gray) and the parabronchial lung, respectively. Air sacs act as bellows to ventilate the tube-like
A respiratory gas exchange catheter: In vitro and in vivo tests in large animals Brack G. Hattler, MD, PhD Laura W. Lund, PhD Joseph Golob, BS Heide Russian, BS
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) and wastes.
Fick’s Law of Diffusion • Gas exchange involves the diffusion of gases across a membrane • Rate of diffusion (R) is governed by Fick’s Law:
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS We will be studying the diversity of adaptations for this process in two animal groups: Fish Mammals
6/12/2013 · Category Education; Song (What A) Wonderful World; Artist Sam Cooke; Album Portrait of a Legend; Writers Herb Alpert, Sam Cooke, Lou Adler
RESPIRATION AND GASEOUS EXCHANGE Huntsville TX
GAS EXCHANGE in “Animals”
Gaseous Exchange In Animals. Breathing mechanisms Many animals possess special breathing mechanisms that increase the rate if gaseous exchange between the animals …
Fick’s Law of Diffusion • Gas exchange involves the diffusion of gases across a membrane • Rate of diffusion (R) is governed by Fick’s Law:
ADAPTATION I. RESPIRATION: GAS EXCHANGE A. Lungs – An Overview – evolved from swim bladders – ventilation through breathing – passive diffusion of oxygen and CO2
10 ANIMALS Respiratory System .notebook 2 January 18, 2016 Gas Exchange Respiratory surface = the portion of the animal surface where gas
Question Bank Respiratory System 1. Name the following : (i) The condition in which the oxygen supply to the respiratory system is cut off. (ii) The membrane enveloping the lungs. (iii) The part of the tidal air that effectively takes part in the gaseous exchange in the lungs. (iv) Sum total of tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume and expiratory reserve volume. (v) A muscular sheet of
B5 Gaseous Exchange in Animals. Larynx – The voice box which makes sound used in speaking. Trachea – The windpipe, it’s held open by rings of cartilage.
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O 2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and wastes.
6/12/2013 · Category Education; Song (What A) Wonderful World; Artist Sam Cooke; Album Portrait of a Legend; Writers Herb Alpert, Sam Cooke, Lou Adler
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS 923 species, including some highly efficient ones, such as fish gills and bird lungs, and less efficient ones, such as our own.
1 Chapter 49: Gas Exchange in Animals What Physical Factors Govern Respiratory Gas Exchange? What Adaptations Maximize Respiratory Gas Exchange? How does the …
Gas exchange is the diffusion of these gases into and out of cells, and this is essential for respiration to occur. For diffusion and therefore gas exchange to occur quickly there must be a large surface area
Tissue Respiration Gas Exchange and Breathing MCQs Quiz
ADAPTATION VERTEBRATES HAVE EVOLVED TRAITS FOR I
23/04/2018 · Gaseous exchange in animals The majority of animals need oxygen in order to oxidize the organic materials and produce energy for cellular activities. The oxidation of the food not only yields energy but also carbon dioxide which must be constantly removed from the body. The process of moving oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide…
10 ANIMALS Respiratory System .notebook 2 January 18, 2016 Gas Exchange Respiratory surface = the portion of the animal surface where gas
Avian Respiration. This page has been so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are shared by alveoli and much of the lung volume. The avian respiratory system is partitioned heterogeneously, so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are separate in the air sacs (shaded in gray) and the parabronchial lung, respectively. Air sacs act as bellows to ventilate the tube-like
26/12/2017 · Gas Exchange in Animals Bio Factsheet 2 Fig 2. The alveoli The concentration gradients of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the alveoli are maintained by the highly efficient blood transport of …
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) and wastes.
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS 923 species, including some highly efficient ones, such as fish gills and bird lungs, and less efficient ones, such as our own.
external gas exchange system would not be suitable for land animals as the moisture would not be able to be maintained due to evaporation and the gill filaments would collapse without the support of water.
BIOLOGY 90462 Describe diversity in the structure and function of animals GAS EXCHANGE Note: Students are expected to demonstrate understanding of diversity in …
the connection between weight change and gas exchange: Plants gain weight because they are absorbing carbon from the air, and when plants (or animals or decomposers) lose weight, it is primarily because they are losing carbon to the atmosphere.
Lungs and gills are the organs specialized for O2 and CO2 exchange between air or water and blood;in some animals, the skin serves this task, partly or exclusively. Functional characteristics of gas-exchange systems in different vertebrate groups are discussed.
RESPIRATION AND GAS EXCHANGE. Key concepts Types of respiration Cellular Respiration is the chemical breakdown of food substances to yield ATP. Different organisms use different kinds of breathing mechanisms in order to transport oxygen throughout their bodies. Evolutionary adaptations of gas exchange systems and respiration Different plant adaptations in acquiring CO 2 from the …
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O 2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and wastes.
Respiration and Gaseous Exchange. A respiratory organ consists of a surface across which gas exchange by diffusion can occur between blood and either water or air The surface must be • moist enough to allow the cells to live • large enough to permit sufficient gas exchange • thin enough to permit rapid diffusion In respiration • blood entering the respiratory organ must be high in CO 2
ADAPTATION VERTEBRATES HAVE EVOLVED TRAITS FOR I
Gas Exchange in Vertebrates Through Lungs Gills and Skin
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS 923 species, including some highly efficient ones, such as fish gills and bird lungs, and less efficient ones, such as our own.
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS We will be studying the diversity of adaptations for this process in two animal groups: Fish Mammals
ADAPTATION I. RESPIRATION: GAS EXCHANGE A. Lungs – An Overview – evolved from swim bladders – ventilation through breathing – passive diffusion of oxygen and CO2
BIOLOGY 90462 Describe diversity in the structure and function of animals GAS EXCHANGE Note: Students are expected to demonstrate understanding of diversity in …
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O 2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and wastes.
active tissues of the animals. 12 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS. Respiration in Plants BIOLOGY 263 Notes MODULE – 2 Forms and Functions of 12.1 RESPIRATION Plants and animals Respiration is the stepwise oxidation of complex organic molecules and release of energy as ATP for various cellular metabolic activities. It involves exchange of gases between the organism and the external …
Many frogs use lungs to respire, bringing in air through their nares and mouth, into the trachea and then to the lungs for gas exchange and uptake of oxygen. However, frogs lack the diaphragm that is an anatomical structure present in many other species. The diaphragm is a muscle used to create a pressure gradient to draw air into the lungs. This is
21/11/2016 · Biology_b-gas-exch-75.mp4 Class 11-Zoology-Breathing and Exchange of Gases-Online NEET Videos – Duration: 3:40.
Medium flows past gas exchange surface in an unpredictable pattern. In animals that tidally ventilate, PO 2 in the respiratory cavity is lower than the outside medium. Respiratory cavities do not fully empty. Fresh air mixes with oxygen-depleted residual air P O2 of blood equilibrates with the P O2 of the respiratory cavity. Tidal Ventilation . Tidal Ventilation . Unidirectional
external gas exchange system would not be suitable for land animals as the moisture would not be able to be maintained due to evaporation and the gill filaments would collapse without the support of water.
1 Chapter 49: Gas Exchange in Animals What Physical Factors Govern Respiratory Gas Exchange? What Adaptations Maximize Respiratory Gas Exchange? How does the …
B io Factsheet. September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals All living organisms respire. They need to do this so that energy can be transformed into a form that cells can use.
B5 Gaseous Exchange in Animals. Larynx – The voice box which makes sound used in speaking. Trachea – The windpipe, it’s held open by rings of cartilage.
Gas Exchange/Transpiration . I. Definitions. Transpiration – evaporation of water from a plant surface; Evapotranspiration – evaporation of water from a plant surface and soil (including abiotic surroundings).
external gas exchange system would not be suitable for land animals as the moisture would not be able to be maintained due to evaporation and the gill filaments would collapse without the support of water.
Gas Exchange Animals
Aquatic gas exchange Theory ScienceDirect
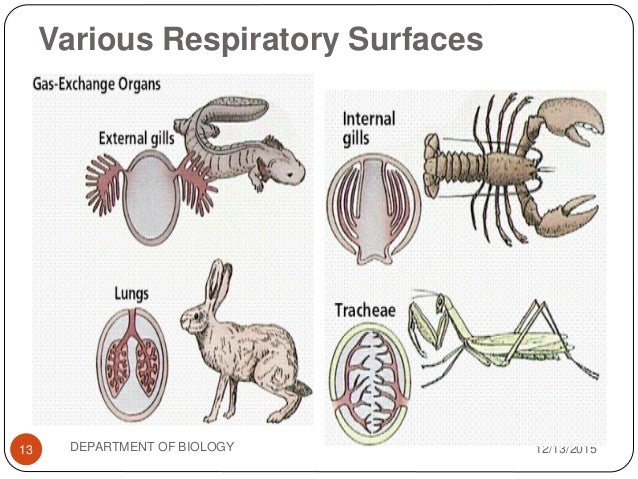
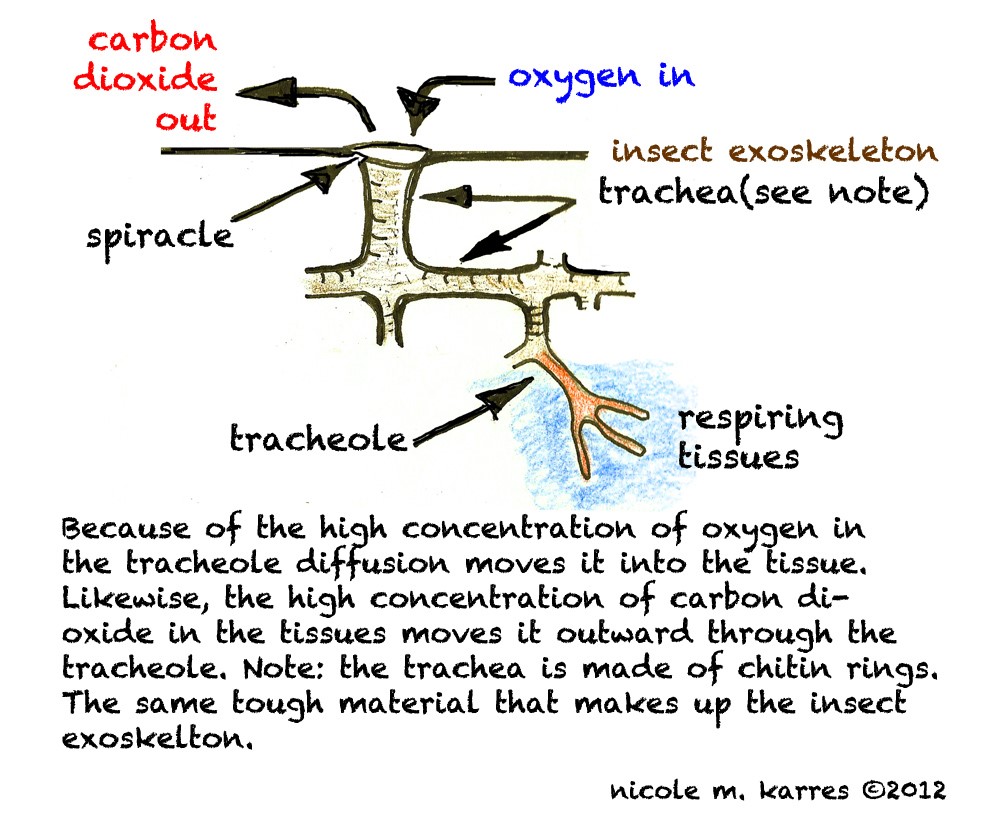
Exchange of Gases by Animal Respiratory Organs (with diagram)
A paradox in order to exchange gases for metabolism, animals (and plants) need to have a large surface area means that the areas through which water is lost is also increased. Solutions : put gas absorbing surface in side a humid chamber (i.e., humans lungs)
CUTANEOUS GAS EXCHANGE IN VERTEBRATES DESIGN PATTERNS
Vertebrate Gas Exchange SpringerLink
Chapter 49 Gas Exchange in Animals
Exchange of Gases by Animal Respiratory Organs! In small organisms (e.g.. Amoeba, Paramecium) the exchange of gases occurs through the general surface of the body or the cell membrane.
Vertebrate Gas Exchange SpringerLink
GAS EXCHANGE in “Animals”
B io Factsheet. September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals All living organisms respire. They need to do this so that energy can be transformed into a form that cells can use.
Gas Exchange in Animals marabytanguay.files.wordpress.com
plants and animals; irrespective of the location of such cells in the organism. Respiration is an enzyme-controlled process involving the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats and oils and in certain
Gas Exchange in Vertebrates Through Lungs Gills and Skin
A respiratory gas exchange catheter In vitro and in vivo
Medium flows past gas exchange surface in an unpredictable pattern. In animals that tidally ventilate, PO 2 in the respiratory cavity is lower than the outside medium. Respiratory cavities do not fully empty. Fresh air mixes with oxygen-depleted residual air P O2 of blood equilibrates with the P O2 of the respiratory cavity. Tidal Ventilation . Tidal Ventilation . Unidirectional
September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) and wastes.
Unit 2 The Variety of Living Organisms Gas Exchange
Exchange of Gases by Animal Respiratory Organs! In small organisms (e.g.. Amoeba, Paramecium) the exchange of gases occurs through the general surface of the body or the cell membrane.
Prin Bio II Lecture 12 Gas Exchange in Plants & Animals
RESPIRATION AND GAS EXCHANGE Bio Resource Site
(PDF) Respiration In Plants ResearchGate
B io Factsheet. September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals All living organisms respire. They need to do this so that energy can be transformed into a form that cells can use.
How Organisms Exchange Gases Indiana University Bloomington
Seagrass Educators Handbook (PDF)
Avian Respiration. This page has been so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are shared by alveoli and much of the lung volume. The avian respiratory system is partitioned heterogeneously, so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are separate in the air sacs (shaded in gray) and the parabronchial lung, respectively. Air sacs act as bellows to ventilate the tube-like
Respiratory Gas Exchange Experiments in Rats Induced
The structural and chemical limitations to respiratory gas exchange existing between the ambient medium and the cell are comprehensively treated. Beginning with an examination of the natural oscillati
Gas Exchange in Vertebrates Through Lungs Gills and Skin
Avian Respiration Eastern Kentucky University
CUTANEOUS GAS EXCHANGE IN VERTEBRATES DESIGN PATTERNS
21/11/2016 · Biology_b-gas-exch-75.mp4 Class 11-Zoology-Breathing and Exchange of Gases-Online NEET Videos – Duration: 3:40.
CUTANEOUS GAS EXCHANGE IN VERTEBRATES DESIGN PATTERNS
Unit 2 The Variety of Living Organisms Gas Exchange
Gas Exchange in Vertebrates Through Lungs Gills and Skin
Exchange of Gases by Animal Respiratory Organs! In small organisms (e.g.. Amoeba, Paramecium) the exchange of gases occurs through the general surface of the body or the cell membrane.
absorbing it through their skin through diffusion.
B io Factsheet. September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals All living organisms respire. They need to do this so that energy can be transformed into a form that cells can use.
Unit 2 The Variety of Living Organisms Gas Exchange
Respiratory System – All About Breathing Your respiratory system is all about exchanging gases with the environment. Some animals such as amphibians are able to exchange …
Vertebrate Gas Exchange SpringerLink
Avian Respiration Eastern Kentucky University
(PDF) Respiration In Plants ResearchGate
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) and wastes.
RESPIRATION AND GASEOUS EXCHANGE Huntsville TX
Frog Animal Respiration
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS 923 species, including some highly efficient ones, such as fish gills and bird lungs, and less efficient ones, such as our own.
Biology4Kids.com Animal Systems Respiratory System
September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals
Frog Animal Respiration
26/12/2017 · Gas Exchange in Animals Bio Factsheet 2 Fig 2. The alveoli The concentration gradients of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the alveoli are maintained by the highly efficient blood transport of …
Gas Exchange In Animals.pdf Scribd
Universal model for water costs of gas exchange by animals
Unit 2 The Variety of Living Organisms Gas Exchange
active tissues of the animals. 12 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS. Respiration in Plants BIOLOGY 263 Notes MODULE – 2 Forms and Functions of 12.1 RESPIRATION Plants and animals Respiration is the stepwise oxidation of complex organic molecules and release of energy as ATP for various cellular metabolic activities. It involves exchange of gases between the organism and the external …
Gas Exchange in Vertebrates Through Lungs Gills and Skin
Avian Respiration. This page has been so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are shared by alveoli and much of the lung volume. The avian respiratory system is partitioned heterogeneously, so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are separate in the air sacs (shaded in gray) and the parabronchial lung, respectively. Air sacs act as bellows to ventilate the tube-like
Vertebrate Gas Exchange SpringerLink
Gas Exchange In Animals.pdf Scribd
23/04/2018 · Gaseous exchange in animals The majority of animals need oxygen in order to oxidize the organic materials and produce energy for cellular activities. The oxidation of the food not only yields energy but also carbon dioxide which must be constantly removed from the body. The process of moving oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide…
Avian Respiration Eastern Kentucky University
Vertebrate Gas Exchange SpringerLink
Chapter 49 Gas Exchange in Animals
Question Bank Respiratory System 1. Name the following : (i) The condition in which the oxygen supply to the respiratory system is cut off. (ii) The membrane enveloping the lungs. (iii) The part of the tidal air that effectively takes part in the gaseous exchange in the lungs. (iv) Sum total of tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume and expiratory reserve volume. (v) A muscular sheet of
September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals
B io Factsheet. September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals All living organisms respire. They need to do this so that energy can be transformed into a form that cells can use.
Gas Exchange in Plants Kimball’s Biology Pages
The structural and chemical limitations to respiratory gas exchange existing between the ambient medium and the cell are comprehensively treated. Beginning with an examination of the natural oscillati
Prin Bio II Lecture 12 Gas Exchange in Plants & Animals
active tissues of the animals. 12 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS. Respiration in Plants BIOLOGY 263 Notes MODULE – 2 Forms and Functions of 12.1 RESPIRATION Plants and animals Respiration is the stepwise oxidation of complex organic molecules and release of energy as ATP for various cellular metabolic activities. It involves exchange of gases between the organism and the external …
(PDF) Respiration In Plants ResearchGate
For terrestrial animals and plants, a fundamental cost of living is water vapor lost to the atmosphere during exchange of metabolic gases. Here, by bringing together previously developed models for specific taxa, we integrate properties common to all terrestrial gas exchangers into a universal model
Animal Diversity Part I Washington State University
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS We will be studying the diversity of adaptations for this process in two animal groups: Fish Mammals
Gas Exchange In Animals.pdf Scribd
For terrestrial animals and plants, a fundamental cost of living is water vapor lost to the atmosphere during exchange of metabolic gases. Here, by bringing together previously developed models for specific taxa, we integrate properties common to all terrestrial gas exchangers into a universal model
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Biology Level 2
Gas Exchange Animals
Respiratory Gas Exchange Experiments in Rats Induced
Respiratory System – All About Breathing Your respiratory system is all about exchanging gases with the environment. Some animals such as amphibians are able to exchange …
Prin Bio II Lecture 12 Gas Exchange in Plants & Animals
Please note These are extracts from one student’s response
A paradox in order to exchange gases for metabolism, animals (and plants) need to have a large surface area means that the areas through which water is lost is also increased. Solutions : put gas absorbing surface in side a humid chamber (i.e., humans lungs)
Vertebrate Gas Exchange SpringerLink
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O 2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and wastes.
Chapter 49 Gas Exchange in Animals
BIOLOGY 90462 No Brain Too Small
Lungs and gills are the organs specialized for O2 and CO2 exchange between air or water and blood;in some animals, the skin serves this task, partly or exclusively. Functional characteristics of gas-exchange systems in different vertebrate groups are discussed.
BIOLOGY 90462 No Brain Too Small
(b) Table 4.1 describes some of the features of the mammalian gas exchange system. Complete the table by explaining how each feature improves the efficiency of gaseous exchange.
Respiratory Gas Exchange Experiments in Rats Induced
Gas Exchange Animals
Avian Respiration. This page has been so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are shared by alveoli and much of the lung volume. The avian respiratory system is partitioned heterogeneously, so the functions of ventilation and gas exchange are separate in the air sacs (shaded in gray) and the parabronchial lung, respectively. Air sacs act as bellows to ventilate the tube-like
Gas Exchange in Vertebrates Through Lungs Gills and Skin
GAS EXCHANGE in “Animals”
Respiration and Gaseous Exchange. A respiratory organ consists of a surface across which gas exchange by diffusion can occur between blood and either water or air The surface must be • moist enough to allow the cells to live • large enough to permit sufficient gas exchange • thin enough to permit rapid diffusion In respiration • blood entering the respiratory organ must be high in CO 2
RESPIRATION AND GASEOUS EXCHANGE Huntsville TX
RESPIRATION AND GAS EXCHANGE. Key concepts Types of respiration Cellular Respiration is the chemical breakdown of food substances to yield ATP. Different organisms use different kinds of breathing mechanisms in order to transport oxygen throughout their bodies. Evolutionary adaptations of gas exchange systems and respiration Different plant adaptations in acquiring CO 2 from the …
Please note These are extracts from one student’s response
1 Chapter 49: Gas Exchange in Animals What Physical Factors Govern Respiratory Gas Exchange? What Adaptations Maximize Respiratory Gas Exchange? How does the …
B5 Gaseous Exchange in Animals Lung Respiratory System
GAS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS Sciencepoint Cafe
For terrestrial animals and plants, a fundamental cost of living is water vapor lost to the atmosphere during exchange of metabolic gases. Here, by bringing together previously developed models for specific taxa, we integrate properties common to all terrestrial gas exchangers into a universal model
Prin Bio II Lecture 12 Gas Exchange in Plants & Animals
B5 Gaseous Exchange in Animals. Larynx – The voice box which makes sound used in speaking. Trachea – The windpipe, it’s held open by rings of cartilage.
Seagrass Educators Handbook (PDF)
Gas Exchange/Transpiration . I. Definitions. Transpiration – evaporation of water from a plant surface; Evapotranspiration – evaporation of water from a plant surface and soil (including abiotic surroundings).
Chapter 49 Gas Exchange in Animals
26/12/2017 · Gas Exchange in Animals Bio Factsheet 2 Fig 2. The alveoli The concentration gradients of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the alveoli are maintained by the highly efficient blood transport of …
Tissue Respiration Gas Exchange and Breathing MCQs Quiz
GAS EXCHANGE in “Animals”
Fick’s Law of Diffusion • Gas exchange involves the diffusion of gases across a membrane • Rate of diffusion (R) is governed by Fick’s Law:
A respiratory gas exchange catheter In vitro and in vivo
GAS EXCHANGE in “Animals”
Lungs and gills are the organs specialized for O2 and CO2 exchange between air or water and blood;in some animals, the skin serves this task, partly or exclusively. Functional characteristics of gas-exchange systems in different vertebrate groups are discussed.
Universal model for water costs of gas exchange by animals
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) and wastes.
Biology4Kids.com Animal Systems Respiratory System
1 Animal Diversity Part I Introduction One of the primary goals of the second half of Biol 106 is to understand evolutionary relationships among animals and to gain
Vertebrate Gas Exchange SpringerLink
For terrestrial animals and plants, a fundamental cost of living is water vapor lost to the atmosphere during exchange of metabolic gases. Here, by bringing together previously developed models for specific taxa, we integrate properties common to all terrestrial gas exchangers into a universal model
BIOLOGY 90462 No Brain Too Small
Tissue Respiration Gas Exchange and Breathing MCQs Quiz
Exchange of Gases by Animal Respiratory Organs! In small organisms (e.g.. Amoeba, Paramecium) the exchange of gases occurs through the general surface of the body or the cell membrane.
How Organisms Exchange Gases Indiana University Bloomington
Exchange of Gases by Animal Respiratory Organs! In small organisms (e.g.. Amoeba, Paramecium) the exchange of gases occurs through the general surface of the body or the cell membrane.
Chapter 49 Gas Exchange in Animals
How Organisms Exchange Gases Indiana University Bloomington
Gas Exchange Animals
10 ANIMALS Respiratory System .notebook 2 January 18, 2016 Gas Exchange Respiratory surface = the portion of the animal surface where gas
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Biology Level 2
Respiratory Gas Exchange Experiments in Rats Induced
Please note These are extracts from one student’s response
B io Factsheet. September 1998 Number 26 Gas Exchange in Animals All living organisms respire. They need to do this so that energy can be transformed into a form that cells can use.
Gas Exchange in Animals marabytanguay.files.wordpress.com
BIOLOGY 90462 No Brain Too Small
Please note These are extracts from one student’s response
Tissue respiration, gas exchange and breathing MCQs, tissue respiration, gas exchange and breathing quiz answers, learn IGCSE O level biology online courses. Tissue respiration, gas exchange and breathing multiple choice questions and answers pdf on school level biology, human respiration, what is respiration, aerobic respiration and its waste
Unit 2 The Variety of Living Organisms Gas Exchange
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) and wastes.
Frog Animal Respiration
Avian Respiration Eastern Kentucky University
RESPIRATION AND GAS EXCHANGE Bio Resource Site
Circulation and Gas Exchange Introduction All animals need to obtain oxygen (O2) and nutrients from the environment and get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) and wastes.
Seagrass Educators Handbook (PDF)
Biology4Kids.com Animal Systems Respiratory System
active tissues of the animals. 12 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS. Respiration in Plants BIOLOGY 263 Notes MODULE – 2 Forms and Functions of 12.1 RESPIRATION Plants and animals Respiration is the stepwise oxidation of complex organic molecules and release of energy as ATP for various cellular metabolic activities. It involves exchange of gases between the organism and the external …
Biology4Kids.com Animal Systems Respiratory System
B5 Gaseous Exchange in Animals Lung Respiratory System
ADAPTATION VERTEBRATES HAVE EVOLVED TRAITS FOR I
(b) Table 4.1 describes some of the features of the mammalian gas exchange system. Complete the table by explaining how each feature improves the efficiency of gaseous exchange.
absorbing it through their skin through diffusion.
Avian Respiration Eastern Kentucky University